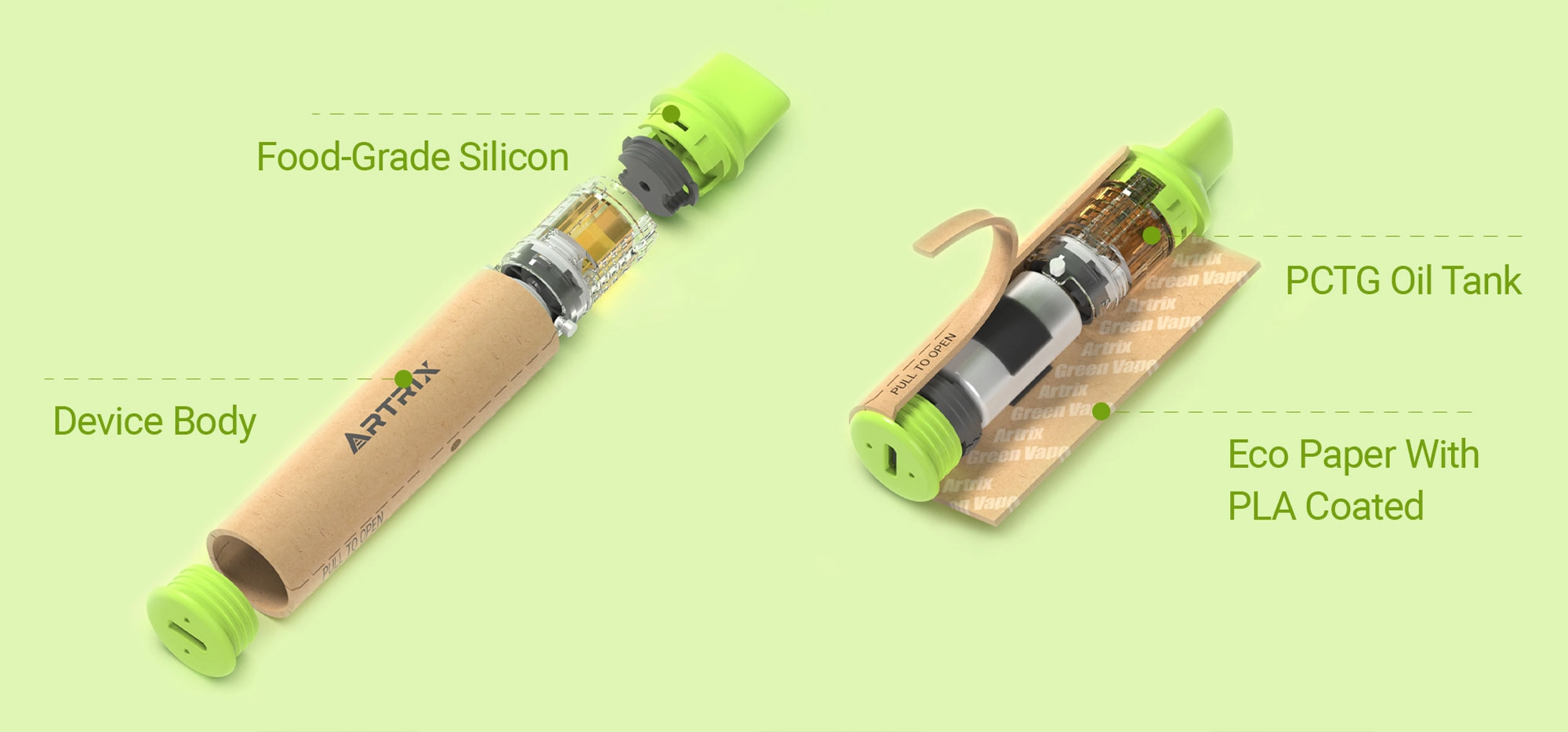
THC vs CBD: Understanding the Key Differences
As discussions about cannabis continue to grow, two of its most prominent components—CBD and THC—are often at the forefront. With the rise of marijuana legalization, it’s important to grasp the key differences between these two compounds, especially how they interact with the body.

The Role of the Endocannabinoid System
Within your body lies a complex biological system known as the endocannabinoid system (ECS). This system plays a crucial role in regulating various functions, including mood, appetite, memory, and pain perception. THC and CBD interact with the ECS, influencing how your body feels and reacts.
Breaking Down the Chemistry: THC vs. CBD
Chemically, THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) and CBD (cannabidiol) share a similar structure—they both have the molecular formula (C₁₁H₁₈O₂) and a molecular mass of 314 grams per mole. However, a key difference lies in their biochemistry: THC has a cyclic ring, while CBD features a hydroxyl group. This seemingly small difference is what determines whether or not a compound will cause a psychoactive effect.
CB1 Receptors and Their Function
To understand the effects of THC and CBD, you need to know about CB1 receptors. These receptors respond to a neurotransmitter called anandamide, which influences feelings of pleasure, motivation, and appetite. This is the same compound that contributes to the euphoric sensation known as a “runner’s high.”
THC’s structure mimics that of anandamide, allowing it to bind easily to CB1 receptors, leading to the sensation of being high. In contrast, CBD’s structure prevents it from fitting into CB1 receptors, which is why it doesn’t induce a high. However, CBD interacts with other receptors in the ECS, providing a range of therapeutic effects without psychoactivity.
A 2011 study garnered attention when it revealed that individuals with social anxiety disorder experienced significant reductions in anxiety when given CBD compared to a placebo. Moreover, various animal studies have highlighted CBD’s potential anti-anxiety and anti-inflammatory benefits, offering explanations for its use in managing anxiety and chronic pain.
Interestingly, while THC has been linked to exacerbating psychotic symptoms, some research suggests that CBD may counteract these effects, highlighting its potential role in mental health treatment.
THC and CBD: A Synergistic Relationship
What happens when you consume both THC and CBD simultaneously? Research shows that CBD can act as an allosteric inhibitor by binding to CB1 receptors and moderating the effects of THC. This means that CBD can actually reduce the intensity of THC’s psychoactive effects. For instance, if you vape cannabis with 25% THC and a negligible amount of CBD (0.1%), you will likely feel a strong high. Conversely, consuming cannabis with 25% THC and 12% CBD may produce a milder, more balanced effect due to CBD’s ability to bind with the CB1 receptor.
Exploring the Future of THC and CBD
THC is the psychoactive compound in cannabis that produces a high, while CBD is non-psychoactive but offers a range of therapeutic benefits. As marijuana legalization continues to spread, more research is likely to emerge, shedding light on the full spectrum of benefits and interactions between these compounds. This ongoing exploration could pave the way for more informed usage, especially in medicinal applications.
FAQs
What is the main difference between THC and CBD?
The key difference is that THC produces a high by binding to CB1 receptors, while CBD does not cause a high but offers therapeutic effects through its interactions with other receptors.
Can CBD reduce the effects of THC?
Yes, CBD can modulate the effects of THC by interacting with CB1 receptors, potentially reducing the intensity of the high.
Are there health benefits to using CBD?
Research indicates that CBD may help alleviate anxiety, chronic pain, and inflammation. However, more studies are necessary to fully understand its therapeutic potential.


















-1.webp)
-1.webp)
-2.webp)