The Science of Cannabis
Cannabis was once associated with terms like marijuana, pot, THC, or weed. However, the recent rise of CBD (cannabidiol) has changed the landscape, as it appears in many products from medicines to supplements, foods, and beauty products. What exactly is CBD, and how does it differ from THC, the compound responsible for the psychoactive effects of cannabis?
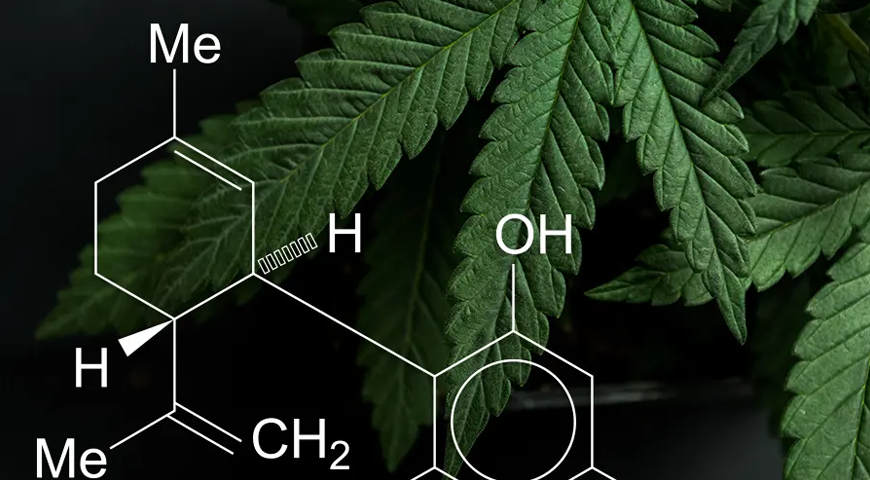
Understanding CBD and THC
CBD or cannabidiol, is one of 150 phytocannabinoids identified in cannabis plants. Unlike THC (tetrahydrocannabinol), CBD is considered non-psychoactive as it does not produce a high. THC, on the other hand, becomes psychoactive only when it is converted from THC-A (tetrahydrocannabinolic acid) through exposure to light, oxygen, and heat.
Cannabis plants all belong to the same species, Cannabis sativa, which includes both marijuana and hemp. The main distinction between these two plants is their concentrations of THC and CBD. Marijuana generally contains 2.5% to 22% THC-A and 0.1% to 12% CBD and Hemp contains 0.3% THC or less, with CBD concentrations averaging around 3.5% but sometimes may reach as high as 20% in certain strains.
The Therapeutic Potential of Cannabinoids
Research on cannabinoids like CBD is still in its early stages, but various compounds show potential benefits. CBG (cannabigerol), another non-psychoactive cannabinoid, may act as a sleeping aid. CBC (cannabichromene) is believed to have sedative properties. THC-V (tetrahydrocannabivarin) and CBN (cannabinol) are psychoactive cannabinoids that are utilized for their pain-relieving effects.
Cannabinoids work by binding to cannabinoid receptors in the central nervous system—primarily CB1 receptors in the brain and CB2 receptors in the immune system. THC binds effectively to CB1 receptors, which modulate non-essential memories, contributing to feelings of relaxation and euphoria.
CBD, on the other hand, does not bind directly to CB1 receptors. Instead, it is believed to influence inflammation, relieve pain, and reduce anxiety, making it a popular compound for therapeutic use.
Conclusion
Cannabinoids represent a new frontier with potential to treat various ailments, from anxiety, migraines, PTSD, and blood pressure. However, more research is needed to fully understand their effects and potential benefits.
FAQs
What is CBD?
CBD is a non-psychoactive phytocannabinoid found in cannabis that does not produce a high, unlike THC.
How do THC and CBD differ?
THC is psychoactive and can alter mood and perception, while CBD is non-psychoactive and is often studied for its therapeutic potential.
What are some potential benefits of cannabinoids?
Cannabinoids may help treat various ailments, including anxiety, pain, inflammation, and sleep disturbances, but further research is needed to fully understand their effects.


















-1.webp)
-1.webp)
-2.webp)