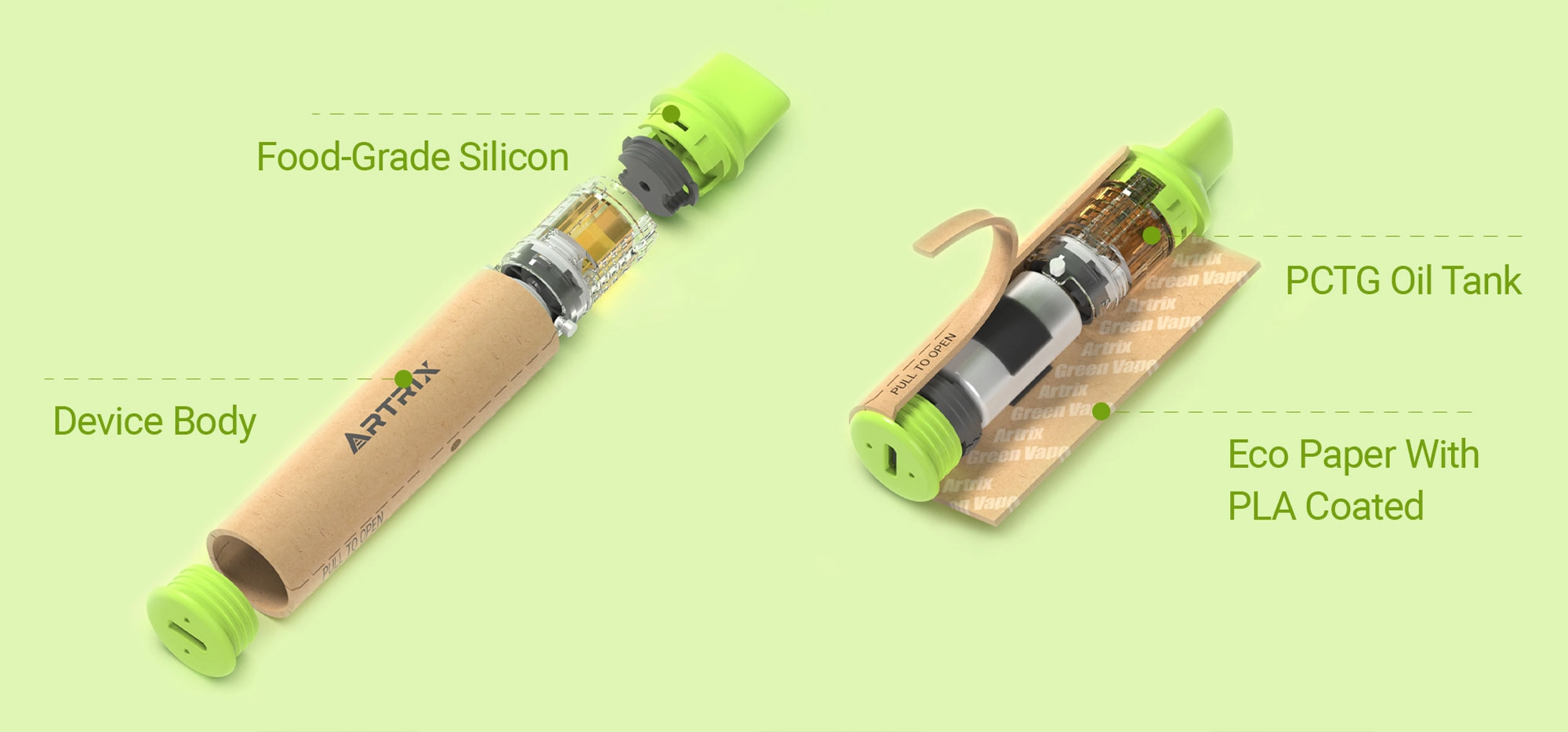
THCa 101: Benefits and Effects
Curious about the buzz surrounding our new THCa vape devices? Wondering, “What exactly is THCa?” You’ve come to the right place. THCa, or Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid, is a fascinating compound found primarily in the raw cannabis plant. If you’ve ever perused lab results for cannabis products and noticed a high THCa content, you might have questions about how it impacts the psychoactive effects of marijuana. You’re certainly not alone in this curiosity.

Understanding THCa: The Non-Psychoactive Precursor
At its core, THCa is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid. This means that consuming raw, fresh cannabis – be it in a juice or tossed into your salad – won’t induce the characteristic “high” associated with marijuana. But the intriguing question remains: how does a non-psychoactive compound like THCa contribute to the euphoric sensation reported by many users?
Decarboxylation: The Key to Cannabis Potency
The answer lies in a transformative process called decarboxylation. This process occurs when cannabis is subjected to heat, whether through smoking, vaporizing, or baking. During decarboxylation, THCa undergoes a chemical change, converting into delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the main psychoactive element in cannabis. Therefore, while THCa in its natural, raw state isn’t intoxicating, its conversion to THC through decarboxylation unlocks a potent experience for cannabis users.
Does THCa Get You High When You Smoke It?
Yes! Have you ever wondered how THCa in cannabis leads to the euphoric highs experienced by users? The key to this transformation lies in understanding the endocannabinoid system (ECS) in our bodies, a critical player in maintaining our internal balance or homeostasis. This system includes two main types of receptors: CB1 and CB2. While THC – the active form of THCa after heating – can directly bind to the CB1 receptors, predominantly located in the brain, THCa itself does not. So using a THCa cart is a great way to vape THCa. Of course there are now THCa disposable vapes on the market as well
This binding of THC to CB1 receptors is what triggers the variety of sensations, mood shifts, and the classic “high” associated with cannabis use. THCa, in its natural state, offers potential health benefits such as anti-inflammatory properties. However, it lacks the ability to interact with the CB1 receptors in the same manner as THC. The transformative process that converts THCa into THC is known as decarboxylation, a crucial step that transforms raw cannabis compounds into a psychoactive experience.
THCA Positive and Side Effects
Positive Effects
1. Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Research demonstrates that THCA possesses significant anti-inflammatory benefits, effectively alleviating symptoms of various inflammation-related conditions. Preclinical studies have found that THCA can inhibit the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, showing therapeutic potential for the following conditions:
- a. Arthritis and rheumatic diseases
- b. Autoimmune diseases (such as lupus)
- c. Inflammatory bowel disease
- d. Chronic pain conditions
Unlike THC, THCA does not produce psychoactive effects, making it an ideal choice for patients who need to maintain mental clarity.
2. Neuroprotective Properties
Multiple studies suggest that THCA may have protective effects on the nervous system. Its potential benefits include:
- a. Reducing oxidative stress damage to neurons
- b. Potentially slowing the progression of neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s
- c. Possible adjuvant therapeutic effects for multiple sclerosis patients
- d. Protecting the brain from ischemic injury
3. Other Potential Benefits
- Anti-emetic effects: Provides relief from chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting
- Appetite regulation: May help improve loss of appetite
- Antioxidant properties: Helps eliminate free radicals in the body
Common Side Effects
THCA is generally considered safe and non-psychoactive in its raw form. However, users should be aware of the following possible side effects:
- Digestive system reactions: Large doses may cause mild stomach discomfort, diarrhea, or indigestion
- Allergic reactions: A small number of people may experience rashes, itching, or other allergic symptoms
- Drug interactions: May interact with certain medications; consult healthcare professionals before use
Usage Precautions
- a. Start with small doses and gradually adjust to find the appropriate individual dosage
- b. Pregnant and breastfeeding women should avoid use
- c. Use with caution before driving or operating machinery
- d. Store away from high temperatures to prevent THCA from converting to THC
How Long Does THCA Stay in Your System?
Metabolism, body fat percentage, usage frequency can influence the duration on how long THCA remains in human’s body system. THCA like many other cannabinoids may linger in the body for days to several weeks depending on each individual’s biological condition and consumption amount. It is important to note that in hair, cannabinoids may be detected for longer-term to up for months.
In standard drug tests, they often target the THC metabolites, not THCA. However, since THCA can convert into THC in the body, it could potentially lead to a positive test result if the conversion is performed internally.

Conclusion
In its raw form, THCa delivers potential therapeutic benefits like anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties without any psychoactive effects, making it ideal for medical users seeking relief without impairment. However, when heated through smoking, vaping, or other decarboxylation methods, THCa transforms into THC, producing the classic euphoric high that recreational users desire. This versatility, combined with the growing availability of THCa vape products and disposables, allows consumers to customize their cannabis experience based on their specific needs and consumption method.


















-1.webp)
-1.webp)
-2.webp)