THCA vs Delta-9: Understanding the Key Differences
In the rapidly evolving world of cannabis science, two compounds frequently come under the microscope: THCA and Delta-9 THC. Though they originate from the same plant, their effects, properties, and legal statuses vary significantly. Understanding their differences is not just for science buffs or cannabis connoisseurs, it’s essential knowledge for anyone navigating the modern cannabis landscape. This article explores their chemistry, how they interact with the body, and what they mean for users and patients alike.
| Feature | THCA | Delta-9 THC |
|---|---|---|
| Full Name | Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid | Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol |
| Found In | Raw, unheated cannabis | Heated/aged cannabis |
| Psychoactive? | No | Yes |
| CB1 Receptor Binding | Cannot bind (blocked by COOH group) | Binds effectively |
| Activation | Requires decarboxylation (heat) | Already activated |
| Common Consumption | Juicing, raw tinctures, topicals | Smoking, vaping, edibles |
| Key Medical Uses | Anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective | Pain relief, appetite stimulation, anti-nausea |
| Federal Legal Status | Federally legal (hemp-derived, <0.3% D9 THC) | Federally controlled (Schedule I, with state exceptions) |
The Crucial Distinction: One Letter, Major Difference
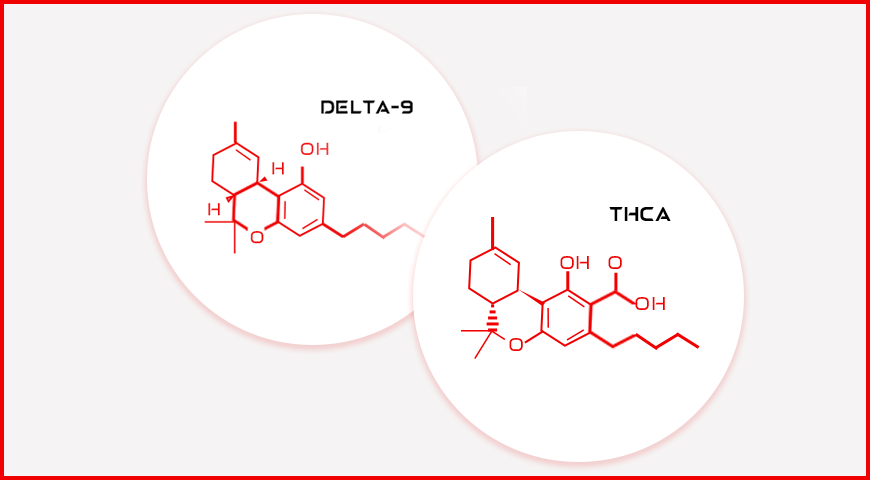
At a glance, THCA and Delta-9 THC appear almost identical, separated by a single letter: the “A.” But this seemingly minor alphabetic difference marks a major chemical divergence. THCA, or tetrahydrocannabinolic acid, is the acidic precursor of Delta-9 THC. Found in raw, unheated cannabis, THCA is non-psychoactive, unlike its neutral counterpart, Delta-9 THC, which famously induces a high.
The difference lies in their molecular structure. THCA contains an additional carboxyl group (COOH), which prevents it from fitting into the brain’s CB1 receptors, responsible for psychoactive effects. Once heat is introduced, this carboxyl group detaches, converting THCA into Delta-9 THC in a process known as decarboxylation.
Raw vs Activated: Cannabis, Cooked and Uncooked
To visualize this difference, imagine a raw potato and a baked one. Both come from the same source, but one is ready to eat, while the other is not. Similarly, raw cannabis is rich in THCA, whereas heated or aged cannabis contains Delta-9 THC. Without decarboxylation, THCA remains in its inactive, acidic form.
This fundamental difference impacts everything from medical applications to recreational effects. While raw cannabis may be juiced for its potential health benefits without inducing a high, only decarboxylated cannabis delivers the euphoric punch associated with smoking, vaping, or edibles.
Unpacking Delta-9 THC: The High Everyone Talks About
Delta-9 THC is the most well-known cannabinoid in the cannabis plant. Its fame stems from its potent psychoactive effects, which make it the primary target for both recreational use and certain medical therapies.
What is Delta-9 THC?
Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol is a cannabinoid characterized by a specific molecular configuration. The “delta-9” refers to the position of a double bond in its carbon chain. This structure allows it to interact efficiently with the endocannabinoid system, especially the CB1 receptors in the brain.
How Delta-9 THC Works in the Body
Delta-9 THC binds to CB1 receptors, which are concentrated in regions of the brain responsible for memory, pleasure, coordination, and time perception. This binding disrupts normal neurotransmitter function and stimulates dopamine release, resulting in feelings of euphoria, relaxation, and altered sensory perception.
The Science Behind the High
The “high” caused by Delta-9 THC stems from its capacity to mimic anandamide, a natural endocannabinoid. When THC binds to CB1 receptors, it not only stimulates dopamine production but also inhibits GABA, a neurotransmitter that normally suppresses dopamine. This double effect amplifies the euphoric experience, leading to the hallmark effects of cannabis intoxication.
THCA: The Unassuming Precursor With Powerful Potential
Often overshadowed by its more famous derivative, THCA is gaining recognition for its non-intoxicating properties and potential therapeutic applications. Though it doesn’t induce a high, its raw form may offer unique benefits worth exploring.
What is THCA?
THCA, or tetrahydrocannabinolic acid, is the most abundant cannabinoid in fresh, unprocessed cannabis. It’s produced in the trichomes of live cannabis plants and is the biochemical precursor to THC. Left unheated, THCA remains stable and non-psychoactive.
Why THCA Doesn’t Make You High
The additional carboxyl group in THCA prevents it from binding effectively to CB1 receptors. As a result, it cannot trigger the psychoactive chain reaction associated with THC. In essence, THCA is chemically incompatible with the brain’s euphoric receptors.
From THCA to THC: The Building Block of the High
All THC begins its life as THCA. When exposed to heat, through smoking, vaping, or baking, the compound undergoes decarboxylation, releasing carbon dioxide and morphing into Delta-9 THC. This transformation is critical for recreational and many medicinal applications.
Raw vs Activated: Two Sides of the Same Coin
While Delta-9 dominates in dried and processed cannabis, THCA rules the fresh, raw variety. Juicing raw cannabis or using unheated tinctures preserves THCA, allowing users to access its benefits without the high. This makes THCA a preferred option for individuals seeking relief without intoxication.
THCA vs THCP
Comparing Their Effects and Strength
Although THCA and Delta-9 THC share a molecular lineage, their effects on the body and mind diverge significantly.
Psychoactive Experience: One Gets You High, One Doesn’t
Delta-9 THC is known for its cerebral effects; euphoria, sensory enhancement, and relaxation. In contrast, THCA in its raw form is entirely non-psychoactive, making it suitable for daytime use and individuals sensitive to intoxication.
Potency and Strength
Delta-9 THC is potent and bioavailable when decarboxylated. THCA, while chemically present in greater amounts in raw cannabis, only expresses its potency after conversion. The difference in bioavailability also means Delta-9 kicks in faster and more noticeably.
Duration and Onset
Delta-9’s effects vary based on consumption method. Smoked or vaped THC typically hits within minutes and lasts 1–3 hours. Edibles take longer—up to 90 minutes—but may last up to 6 hours. THCA, used raw, may offer subtle physiological effects that are less time-sensitive.
Side Effects and Risks
Delta-9 THC can induce dry mouth, red eyes, anxiety, or even paranoia in sensitive individuals. THCA, being non-psychoactive, generally lacks these effects and is considered safer in raw form, particularly for long-term wellness routines.
Medicinal Value: Why Patients Choose One Over the Other
As cannabis gains medical legitimacy, the distinctions between THCA and Delta-9 THC become more clinically relevant.
Medicinal Uses of Delta-9 THC
Approved in various states and countries for medical use, Delta-9 is valued for:
- – Alleviating chronic pain
- – Stimulating appetite in patients with cancer or HIV/AIDS
- – Reducing nausea, particularly during chemotherapy
- – Easing muscle spasms in conditions like multiple sclerosis
- – Enhancing mood and sleep quality
THCA’s Therapeutic Promise
Emerging research suggests THCA has therapeutic potential, especially in:
- – Reducing inflammation, particularly in arthritis or autoimmune disorders
- – Protecting neurons, possibly aiding in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s
- – Acting as an antiemetic for nausea relief
- – Slowing cancer cell proliferation
- – Managing pain without cognitive impairment
Consumption Methods
Understanding how to consume each compound enhances their effectiveness and ensures safe usage.
Delta-9 THC Products
Delta-9 is widely available in multiple forms:
- – Smoked flower
- – Vape cartridges
- – Edibles (gummies, chocolates)
- – Tinctures and oils
- – Capsules and transdermal patches
Each method offers different onset times and duration of effects.
THCA Consumption
Because THCA is heat-sensitive, it’s typically consumed raw:
- – Fresh cannabis juice
- – Raw tinctures or capsules
- – Topicals (for localized relief)
- – THCA crystalline (a purified extract)
- – THCA vapes
THCA products like crystalline concentrates can be consumed raw, but are often heated through dabbing or vaping, which converts them to THC and produces psychoactive effects.
Legal Status: The Gray Area
Legal considerations around cannabis vary widely, and knowing the difference between THCA and Delta-9 can help consumers stay compliant.
Regulatory Overview
Under the 2018 Farm Bill (extended through 2025 via the American Relief Act), hemp-derived products are federally legal if they contain no more than 0.3% Delta-9 THC by dry weight. Since the statute references only Delta-9 THC in finished products, THCA technically falls outside this restriction at the federal level.
However, enforcement varies by state. Some states measure total THC potential, including THCA, while others only test active Delta-9 content. Medical and recreational legality adds another layer of complexity.
Staying Safe: Usage Guidelines
No matter the compound, responsible consumption is key to maximizing benefits while minimizing risks.
Dosing Tips
For Delta-9 THC, start low and increase gradually, especially with edibles. New users might begin with 2.5 mg to 5 mg. THCA lacks psychoactivity, but dosage can still affect therapeutic outcomes, particularly with extracts or capsules.
Interaction with Other Medications
Cannabinoids can interact with prescription drugs, especially those affecting liver enzymes. Consult a healthcare provider before combining cannabis with medications.
Final Thoughts: Two Paths, One Plant
Though THCA and Delta-9 THC share a common origin, their paths diverge dramatically in both effects and applications. Delta-9 is the celebrated psychoactive compound that has shaped the cannabis culture for decades. THCA, meanwhile, is emerging as a medicinal powerhouse that offers healing without the high.
Whether you’re a patient, a recreational user, or simply curious, understanding the nuances between these cannabinoids empowers informed choices and safer experiences.

















-1.webp)
-1.webp)
-2.webp)