What is THCA ?
THCa (tetrahydrocannabinolic acid) is a non-intoxicating cannabinoid found abundantly in raw and fresh cannabis plants. Unlike its well-known counterpart THC, which produces the characteristic “high” associated with cannabis use, THCa doesn’t cause psychoactive effects. This acidic precursor serves as the primary form of THC in living cannabis plants, only converting to the psychoactive compound through a process called decarboxylation when exposed to heat, light, or time.
The biosynthesis of THCa occurs naturally within the trichomes—the tiny, crystal-like structures covering cannabis flowers and leaves. The plant produces THCa through a complex enzymatic pathway beginning with cannabigerolic acid (CBGA), often referred to as the “mother of all cannabinoids.” Through the action of THCa synthase enzyme, CBGA is converted into THCa, which serves multiple functions for the plant, including protection against insects, UV radiation, and environmental stressors. The concentration of THCa in cannabis varies significantly based on genetic factors, growing conditions, cultivation methods, and harvest timing, with some strains producing levels exceeding 20% in dried flower.
The key to understanding why THCa remains non-psychoactive lies in its molecular structure. THCa contains a carboxyl group (COOH) attached to its molecular framework, making it too large and polar to effectively cross the blood-brain barrier or bind to CB1 receptors in the brain—the primary mechanism through which THC produces its psychoactive effects. However, when cannabis is heated during smoking, vaping, or cooking (typically at temperatures above 220°F or 104°C), the carboxyl group is removed through decarboxylation, transforming THCa into the smaller, more lipophilic THC molecule that readily interacts with the endocannabinoid system. This structural transformation explains why consuming raw cannabis doesn’t produce intoxication, while heated cannabis products do, making this knowledge essential for both medical patients seeking specific therapeutic effects and cannabis processors aiming to control product potency.
THCa vs Other Compounds – Quick Guide
Understanding how THCa compares to other cannabis compounds helps consumers make informed choices about their cannabis experience.
THCa vs THC
THCa is less potent than THC in its raw form. When heated (smoking, vaping, cooking), THCa converts to THC through decarboxylation, becoming psychoactive. This gives users control over their experience – non-intoxicating when raw, psychoactive when heated.
THCa vs Delta-9 THC
Delta-9 THC is what THCa becomes when heated. It’s highly potent with strong intoxicating effects, euphoria, and sensory changes – perfect for recreational use.
THCa vs Delta-8 THC
Delta-8 THC offers milder effects than Delta-9. It’s not directly converted from THCa but created by chemically altering CBD or Delta-9 THC.
THCa vs THCp
THCp is a newer compound (discovered 2019) that’s potentially much more potent than regular THC. It produces stronger body effects and higher intoxication than THCa.

Is THCA Legal? Understanding the Legal Landscape
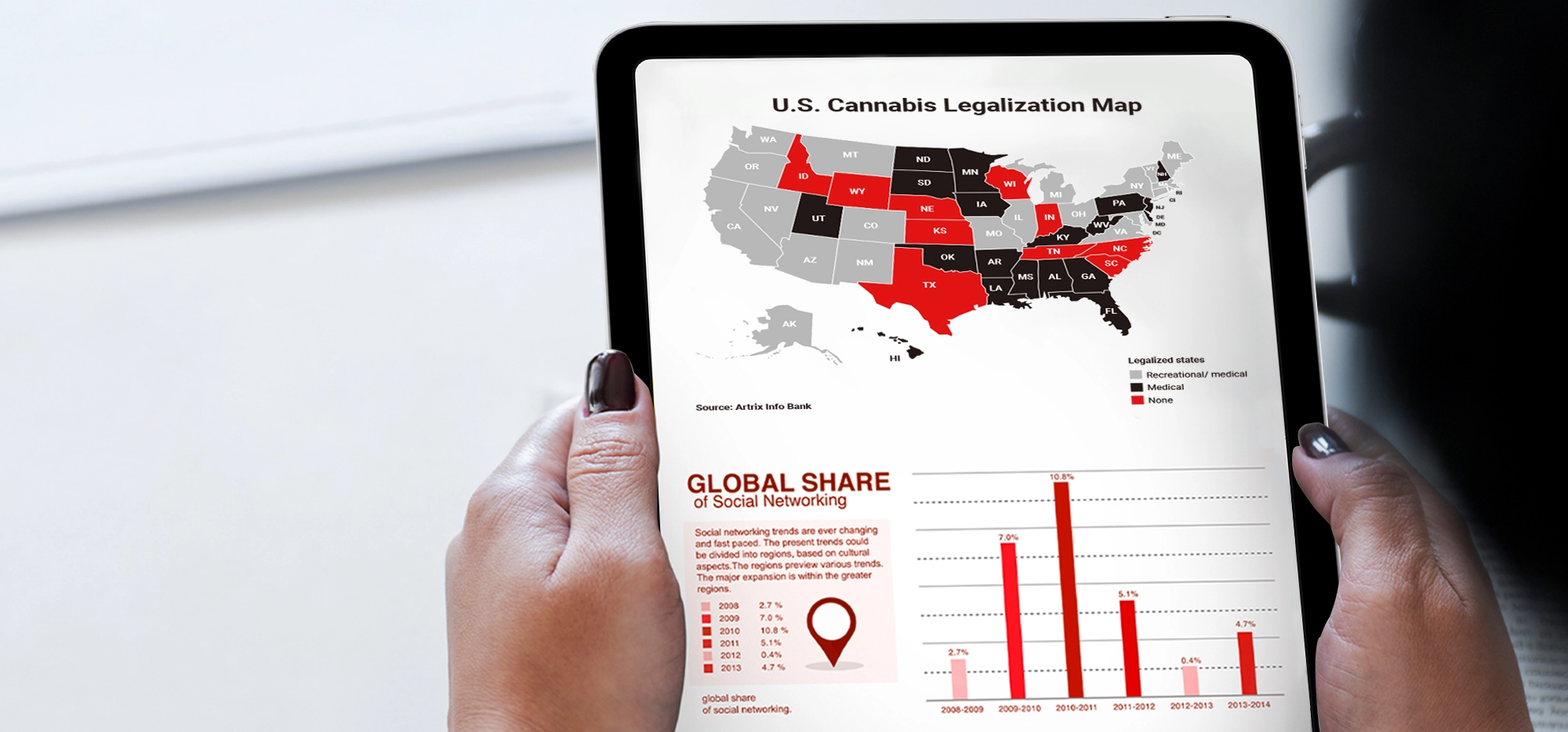
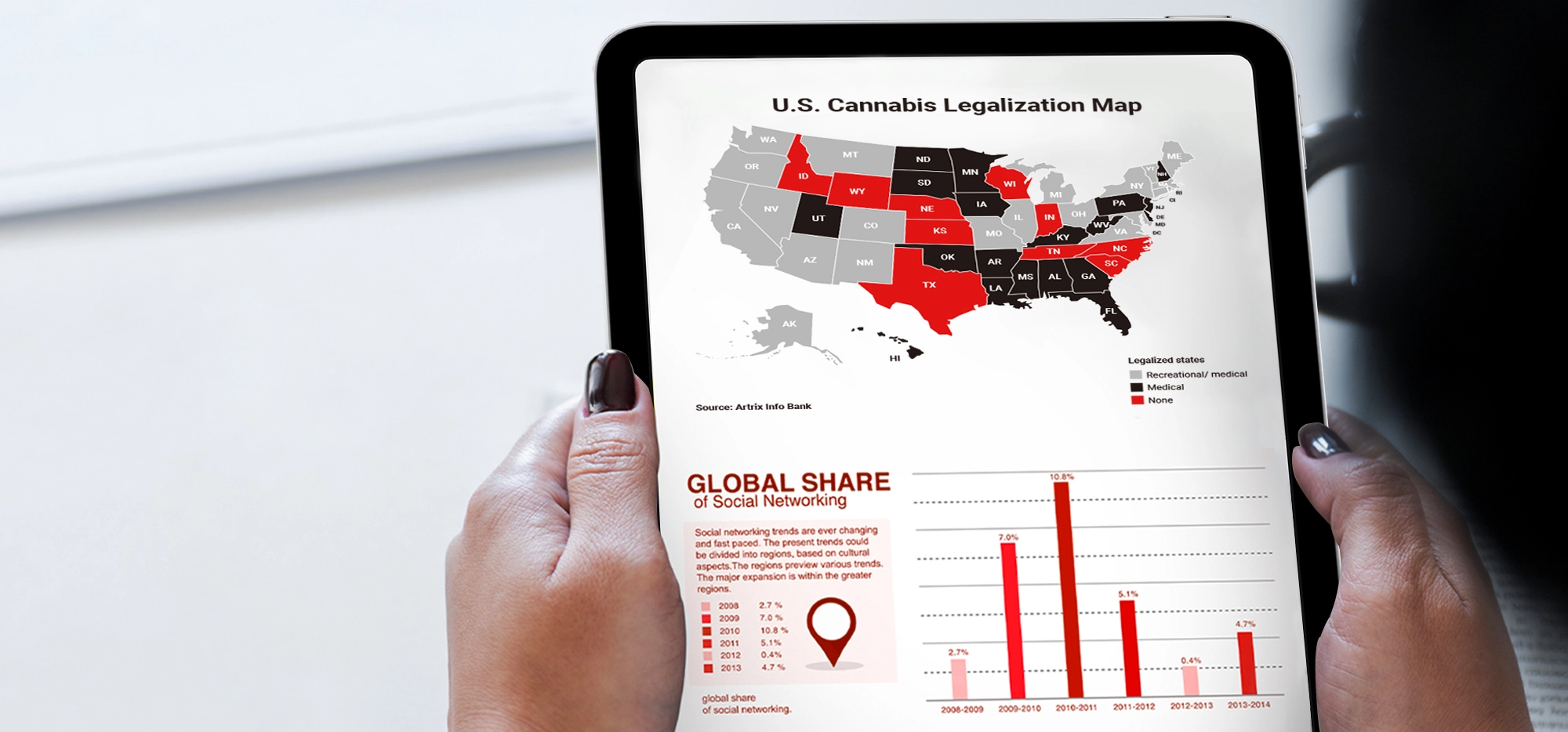
THCA (Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid) exists in a legal gray area in the United States, technically falling under the protection of the 2018 Farm Bill as a hemp-derived compound, provided it contains less than 0.3% Delta-9 THC after decarboxylation. While federally it’s not classified as a controlled substance on its own, individual states have varying regulations—Texas allows THCA within state borders with proper testing, Florida follows federal guidelines requiring less than 0.3% THC content, and Georgia recently tightened restrictions with Senate Bill 494 mandating post-decarboxylation testing. The key legal consideration is that THCA converts to THC when heated, which is why many states require testing to ensure the total THC content remains below legal limits. Given the evolving nature of cannabis legislation, it’s essential to check current federal and state laws before purchasing or using THCA products.
THCA Common Forms
Raw Cannabis
Description: THCA exists naturally in abundance in all raw or unheated cannabis flowers and leaves.
How to use: Added to smoothies, salads, or juices to enhance therapeutic benefits without producing a high.
THCA Crystalline (Isolate)
Description: A highly purified form of THCA with a crystalline structure (often called “diamonds”) that can reach up to 99% purity.
How to use: Used for medicinal purposes through dabbing or sprinkling onto food, providing therapeutic benefits without THC’s psychoactive effects.
THCA Tinctures
Description: Liquid extracts made by soaking cannabis in alcohol or other solvents, resulting in high THCA concentration.
How to use: Administered under the tongue or mixed into drinks; provides non-psychoactive benefits with easy, precise dosing.
THCA Capsules
Description: Pre-measured capsules or softgels containing THCA, often combined with a carrier oil for better absorption.
How to use: Taken orally as a daily supplement for consistent non-psychoactive therapeutic effects.
THCA Topicals
Description: THCA-infused creams, balms, and lotions designed for external application.
How to use: Applied directly to skin for localized pain or inflammation relief without psychoactive effects.
THCA Edibles
Description: Food products like gummies, chocolates, and other treats infused with THCA.
How to use: Consumed orally for therapeutic benefits; ideal for those seeking medicinal effects without intoxication.
THCA Juices
Description: Fresh juice extracted from raw cannabis leaves, preserving the THCA content.
How to use: Consumed as a beverage for non-psychoactive health benefits and nutritional value.
THCA Patches
Description: Transdermal patches that deliver THCA through the skin over an extended period.
How to use: Applied to clean skin for slow, sustained release of THCA, providing continuous relief for pain or inflammation.
What THCA Products can you Buy?
You can find various THCA products on the market today, each offering unique benefits:
1. THCA Flower
This is the most natural form of cannabis. Cannabis Flower is harvested raw and is popular for its high THCA levels. It’s chosen by those who want the health benefits of cannabinoids without the high. This form is great for reducing inflammation and nausea and for those interested in the raw properties of the plant.
2. THCA Cookies and Gummies
Cookies and gummies infused with THCA provide a precisely dosed and convenient way to consume cannabis. These edibles allow users to easily manage their dosage while enjoying the therapeutic benefits in a tasty and discreet form. This type of gummies is especially popular among medical and wellness users seeking a flavorful and portable cannabis option.
3. THCA Concentrates
These are highly potent extracts made for vaporization or dabbing. Just a small amount can have a strong effect, making them a cost-effective choice. Options like diamonds, live resin, and bubble hash offer various characteristics for different preferences.
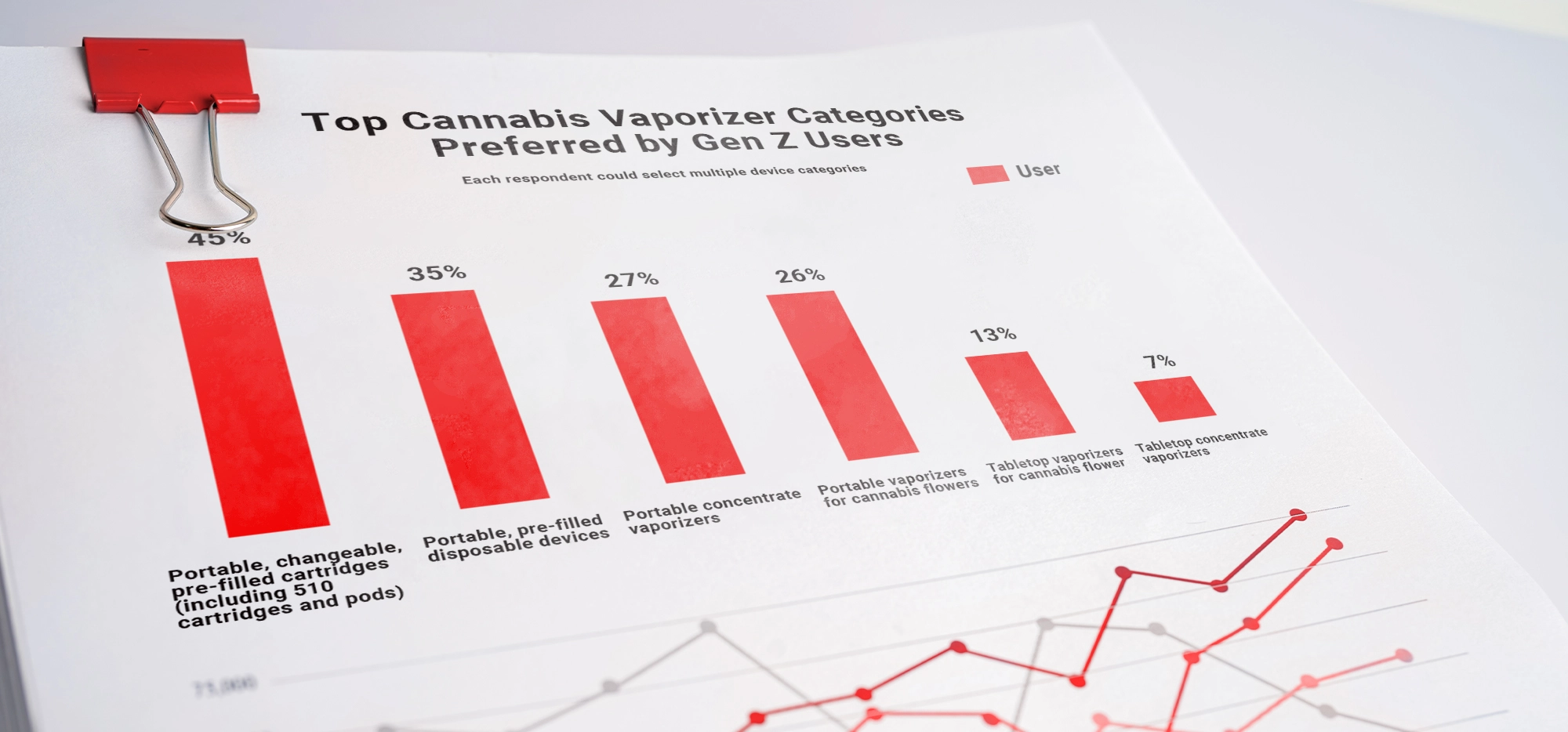
4. THCA Vapes
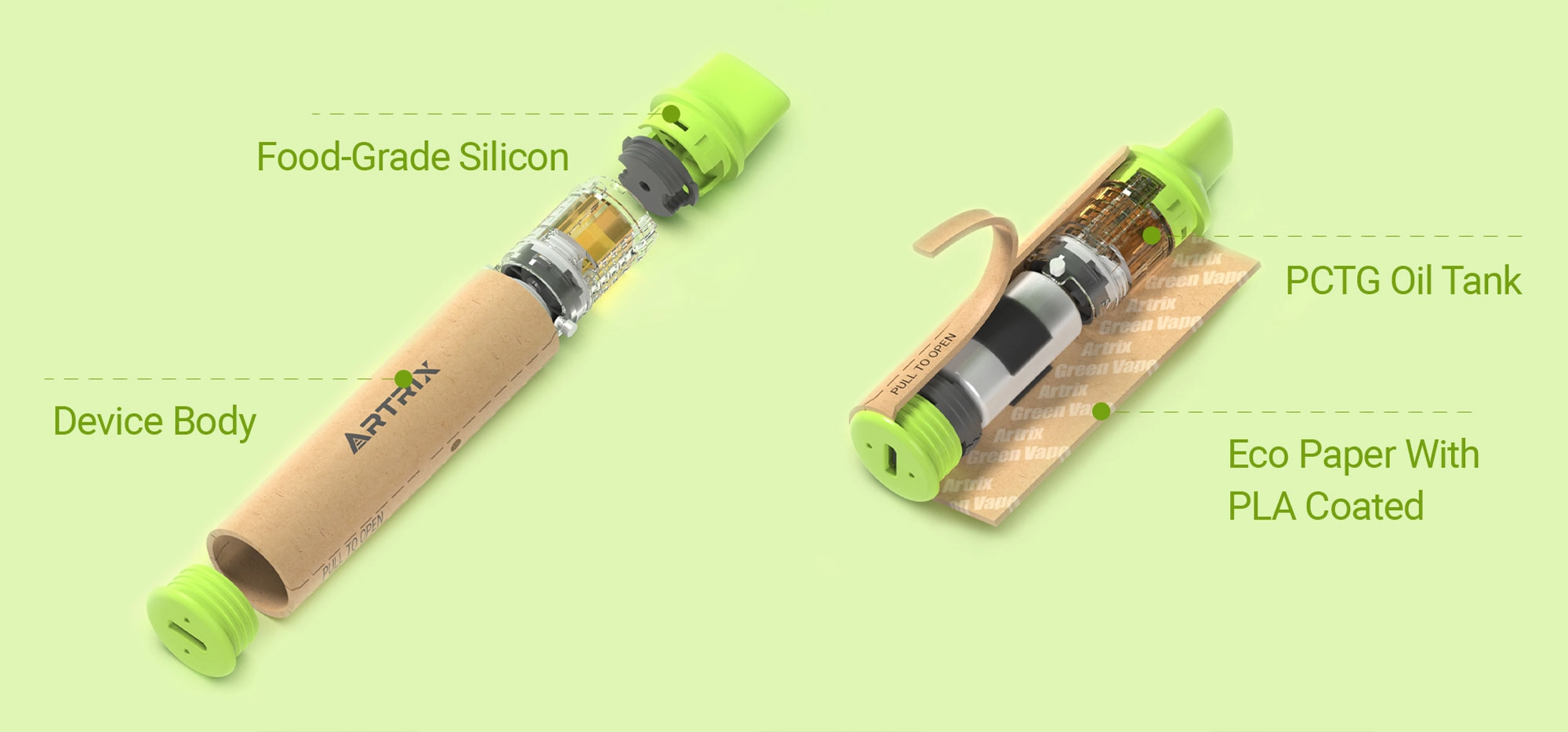
THCA vapes come in a variety of forms, including cartridges, which require a separate battery and allow you to change flavours, and disposables, which are pre-filled, portable and ready to use straight out of the box. These devices offer a clean, controlled release, converting to THC when heated for fast-acting relief and pleasure.
Artrix’s introduction of the DabGo, a disposable dab pen specifically designed for this cannabinoid, represents a significant advancement, providing precise heating and an enhanced user experience.

5. Pre-rolls
Pre-rolls offer a traditional smoking experience but with the benefits of THCA. It also have a reduced risk of overconsumption. Because THCA is non-psychoactive, it’s less likely that individuals will accidentally consume too much and experience unwanted side effects. This is especially important for novice cannabis users who may not be familiar with the effects of THC and may accidentally consume too much.
Does THCa Get You High When You Smoke It?
Yes, but only after it’s heated. THCa itself doesn’t produce a high because it can’t bind to CB1 receptors in your brain. When you smoke or vape THCa, heat converts it to THC through a process called decarboxylation. This activated THC then binds to CB1 receptors, creating the euphoric effects cannabis users experience.For a more detailed exploration of THCa’s effects and mechanisms, you can read our comprehensive guide on this topic.
How to Use THCa?
THCa offers various forms and methods of use, each with its own characteristics and effects. Here’s a breakdown of how you can incorporate THCa into your routine:
1. THCa Flowers
A common and straightforward method of using THCa is through raw cannabis consumption. You can eat it as is, though many prefer adding it to juices or smoothies for improved taste and efficacy. Consuming raw cannabis flowers provides the benefits of THCa without psychoactive high. However, when the flower is smoked or vaporized, the heat triggers the conversion of THCa into THC, leading to the well-known euphoric effects.
2. THCa Concentrates Popular Forms Included
For a more potent experience, you can turn to THCa concentrates, which have a higher concentration of cannabinoids.
2.1 THCa Crystalline
Renowned for its purity, this crystallized form of THCa transforms into THC upon exposure to heat. Whether you’re smoking a joint, using a bong, vaping with a Artrix vape device, or dabbing with DabGo, the heat involved converts THCa to THC, resulting in a potent high.
2.2 THCa Resin and Rosin
Made by freezing the cannabis plant immediately after harvesting and extracting using a solvent, live resin captures the plant’s original flavor and high THCa content. When heated, as in dabbing or vaping, it offers an intense experience.This solvent-free concentrate is produced by applying heat and pressure to cannabis material. Rosin, particularly from high-THCA strains, yields a strong effect when heated, making it a favorite for those seeking a potent experience.Click to learn more about live rosin and resin.
2.3 THCa Tinctures and Topicals
While often overshadowed by CBD, THCa is also available in tinctures and topicals. These products are designed to be part of a daily wellness routine, similar to taking vitamins or using after physical activity for relief. They offer a way to experience the benefits of THCa without psychoactive effects.
THCa distillate.
Conclusion
As research unveils more therapeutic benefits and laws continue to adapt, understanding THCa’s unique properties becomes essential for anyone seeking to make informed cannabis choices, whether for health or recreation.


















-1.webp)
-1.webp)
-2.webp)