THCA vs THCP: Exploring the Extremes of the Cannabinoid Spectrum
As the cannabis industry evolves, the focus has shifted beyond the usual suspects like CBD and Delta-9 THC to more specialized and potent compounds. Two such cannabinoids, THCA (Tetrahydrocannabinolic Acid) and THCP (Tetrahydrocannabiphorol), are at the center of scientific and consumer curiosity.Though both originate from the cannabis plant, their effects, structures, and benefits differ dramatically.
Unpacking the Cannabinoids: What Are THCA and THCP?
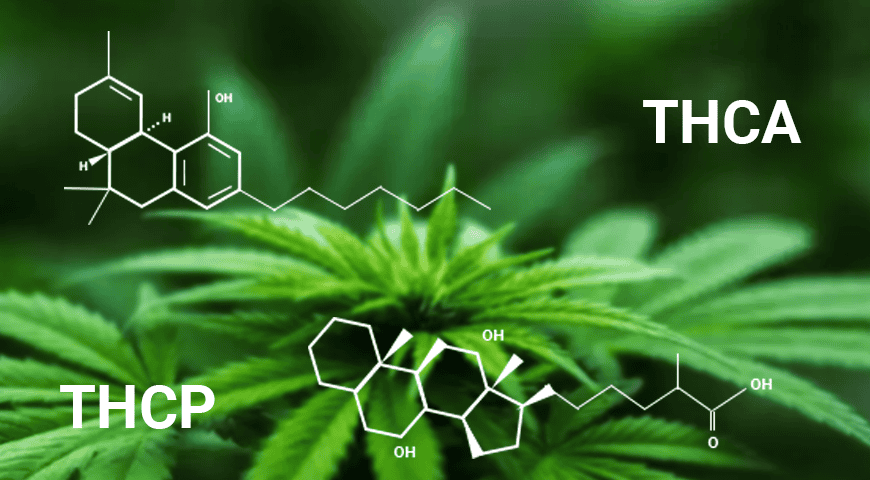
THCA vs THCP
Cannabis is a botanical powerhouse comprising over 100 known cannabinoids, chemical compounds that interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system. Among these, THCA and THCP stand out for their contrasting properties. THCA is the non-psychoactive acid form of THC found in raw cannabis, while THCP is a rare but extremely potent psychoactive compound.
The interest in these two cannabinoids has surged thanks to advanced extraction techniques and new research. Scientists and wellness seekers alike are exploring how these cannabinoids might reshape therapeutic cannabis use, especially given their unique biological behaviors.
THCA: The Gentle Precursor with Hidden Potential
THCA, short for Tetrahydrocannabinolic Acid, is abundant in freshly harvested cannabis. Unlike THC, it does not cause intoxication in its raw form. It is the acidic precursor to Delta-9 THC, the well-known psychoactive compound.
What makes THCA interesting is its transformation via decarboxylation, a process triggered by heat that converts THCA into THC. This is why raw cannabis doesn’t get you “high” unless it’s smoked, vaped, or cooked.
THCP: The New Frontier in Psychoactivity
Discovered in 2019 by Italian researchers, THCP (Tetrahydrocannabiphorol) has shaken the cannabis world. What sets it apart is its chemical affinity for the CB1 receptor—estimated to be 33 times stronger than traditional THC. This means even small doses can yield intense effects.
THCP is found in trace amounts in cannabis, but most of what’s available on the market is synthesized from hemp-derived CBD using a process known as isomerization. This high potency makes THCP both a promising therapeutic compound and one that demands cautious use.
Molecular Blueprints: Chemical Structure and Key Differences
THCA: The Acidic Cannabinoid
THCA’s molecular structure includes a carboxyl group, which is responsible for its non-psychoactive nature. This acidic group makes it stable in raw plant form but also prone to decarboxylation when exposed to light or heat. Its structure defines it as a precursor rather than an active agent, pending its conversion into THC.
THCP: Built for Binding
THCP’s defining structural characteristic is its seven-carbon alkyl side chain, compared to Delta-9 THC’s five-carbon chain. This longer chain increases its binding affinity with the body’s CB1 receptors, amplifying its effects significantly. This enhanced interaction explains THCP’s profound psychoactive potential, even at micro doses.
Comparing Their Effects: Potency and Psychoactivity
THCA’s Subtle Effects
In its raw form, THCA is non-intoxicating, making it ideal for users seeking the health benefits of cannabis without the “high.” Once heated, THCA converts to THC, unlocking euphoric effects, but many consumers use it raw for anti-inflammatory or neuroprotective purposes. Its gentle nature appeals to both new users and medical patients.
THCP: A Heavyweight Among Cannabinoids
THCP delivers powerful effects; euphoria, relaxation, altered sensory perception, and sedation. These effects can be overwhelming for unseasoned users, especially since it binds more aggressively to CB1 receptors than Delta-9 THC. Users often describe a more intense and longer-lasting high.
Strength Showdown: Potency in Practice
When comparing THCA vs THCP, the contrast in potency is stark. THCA requires activation to become psychoactive, while THCP is active in its natural form. THCP’s effects come on quickly and can last significantly longer than THC. For those seeking relief without psychoactivity, THCA is ideal. For intense recreational or severe therapeutic use, THCP may offer advantages, but with risks of overconsumption if not carefully dosed.
Healing Potential: Medical and Wellness Applications
THCA’s Therapeutic Reach
THCA is increasingly recognized for its anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, and antiemetic properties. Many users consume THCA-rich products for arthritis, multiple sclerosis, and nausea without experiencing cognitive impairment. It also shows promise in pain relief and muscle spasm control, making it a valuable tool for daytime use.
THCP’s Medical Possibilities
THCP’s extreme potency means it could offer robust pain relief, particularly for patients with chronic conditions. Its sedative properties may help with insomnia or anxiety, while early research suggests appetite-stimulating potential. However, due to its strength, THCP should be used with medical supervision, especially in high doses or for first-time users.
From Lab to Shelf: How They’re Made
THCA: Careful Extraction to Preserve Purity
Because heat can convert THCA to THC, low-temperature extraction methods are crucial. Popular techniques include diamond mining, which isolates THCA crystals, and flash chromatography, which separates cannabinoids efficiently. Proper quality control ensures the acidic form is retained until consumption.
THCP: Synthetic Solutions to a Rare Compound
Natural THCP is scarce, so commercial products usually rely on synthetic production from CBD through isomerization. This transformation demands advanced lab conditions and rigorous purification to meet safety and purity standards. The high cost of THCP production reflects these complex requirements.
Ways to Enjoy: Consumption Methods Compared
When choosing consumption methods, the key distinction lies in their effects: THCA offers therapeutic benefits without intoxication through raw consumption, while THCP delivers intense psychoactive experiences through traditional cannabis products that require careful dosing.
Consuming THCA
THCA can be consumed in raw forms such as juiced cannabis leaves, or in concentrated products like THCA diamonds. It’s also available in tinctures and oils, often labeled as “non-decarboxylated” to preserve its original state. Users who want medicinal effects without psychoactivity often favor this route.
Consuming THCP
THCP lends itself to more traditional cannabis products, including vapes, edibles, gummies, and tinctures. Due to its high potency, dabbing concentrates with THCP is reserved for experienced consumers. Always start with low doses, as the intensity can be more than anticipated.
Legality and Market Presence
Federal Status in the U.S.
Both THCA and THCP are hemp-derived cannabinoids, which means they often fall under the umbrella of the 2018 Farm Bill, provided they contain less than 0.3% Delta-9 THC. However, the legal landscape is constantly evolving, and legal interpretations vary widely.
Legal Patchwork by State
While federal guidelines offer a foundation, state laws differ. Some states have banned certain hemp-derived psychoactives, including Delta-8, Delta-10, and potentially THCP. THCA may also be restricted when it can be converted to THC through heating.
Market Access and Age Limits
Both cannabinoids are increasingly available in online and retail dispensaries. THCA-rich products tend to be marketed for wellness, while THCP is often framed for high-potency recreational use. Age restrictions typically apply, often limiting access to individuals 21 and older, depending on state law.
Health, Safety, and Responsible Use
THCA: Safe and Mild
THCA has a low side effect profile in its raw form, but users should exercise caution when heating it, as it becomes psychoactive THC. Drug interactions are rare but possible. Pregnant and breastfeeding individuals should avoid THCA due to insufficient safety data.
THCP: Not for the Faint of Heart
Due to its potency, THCP can cause intense psychoactive effects even at small doses. Reported side effects include anxiety, paranoia, and motor impairment. Frequent use may lead to tolerance or psychological dependency. First-time users should approach THCP with caution.
Best Practices for Consumption
No matter the cannabinoid, a “start low and go slow” strategy is vital, especially with compounds like THCP. Users should closely monitor effects and avoid mixing with other intoxicants. Keeping a journal of doses and effects can help fine-tune usage and avoid adverse experiences.
Choosing Between THCA and THCP: What’s Right for You?
Choosing between THCA and THCP depends largely on your goals and experience. If you’re looking for non-intoxicating wellness support, THCA offers a clear path. For experienced users seeking powerful psychoactive effects, THCP might be more suitable, provided it’s used with care.
Some advanced users even combine both for a tailored effect: THCA for daytime use and THCP for evenings or intense relief. However, such combinations should be approached mindfully and ideally under medical guidance.
Final Thoughts: Navigating the Future of Cannabinoids
The world of cannabinoids is more nuanced than ever before. In the debate of THCA vs THCP, we’re not dealing with two versions of the same molecule, but rather two vastly different compounds with distinct roles in wellness and recreation.
THCA serves as a safe, therapeutic agent for users avoiding intoxication, while THCP pushes the envelope of what cannabis can do in terms of psychoactive potency. As research continues and access expands, both cannabinoids will likely play increasingly specific roles in consumer choices and medical cannabis protocols.
Whether you’re a curious consumer, medical patient, or industry professional, understanding the chemical, legal, and experiential contrasts between THCA and THCP is essential to making informed decisions in the ever-expanding cannabis landscape.
















-1.webp)
-1.webp)
-2.webp)